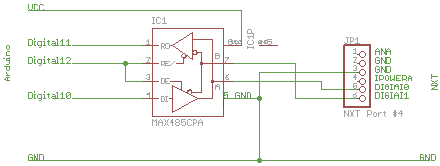
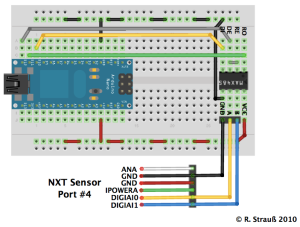
An Arduino sketch, a NXC sample and hardware setup
for RS-485 communications between a
LEGO Mindstorms NXT and an Arduino via a MAX 485
Hardware:
— NXT
— Arduino Nano V3
— MAX 485 CPA
— Breadboard
— Wires
Programming Environment:
— NXT enhanced firmware 1.28
— NXC nbc-1.2.1.r1
— Arduino 0018
— Mac OS X 10.6.3
Notes:
— I used an Arduino Nano V3, any stock Arduino should do it also
— The wiring is simplistic, not optimized for safety/fault tolerance, since I am no electronic expert
— Inspired by Early stage RS 485 with MAX485 in the Arduino forums and RS485 to RS232 Adapter in the nxtasy.org forums
— The serial functions of the Arduino code are stripped down/hacked up
from the old SoftwareSerial library
— The wire from the NXT-connector ground to Arduino ground (to build a common one) is not necessary.
It can be safely left off (per definitionem of RS-485 I think).
— I tested this for baudrates between 9600 and 57600; higher rates don’t work!
Schematics:
baudrate.h:
#define RS485_BAUD 57600
NCX Program: (Screenshot)
#include "baudrate.h"
#define TOWAIT 2000
#define MSG "Hello Arduino "
// -------------------------------------------------------------
void printMsg(byte inbuffer[], int cnt) {
TextOut(0, LCD_LINE3, " Baud");
NumOut(0, LCD_LINE3, RS485_BAUD);
TextOut(0, LCD_LINE5, "l= cnt= ");
NumOut(12, LCD_LINE5, ArrayLen(inbuffer));
NumOut(60, LCD_LINE5, cnt);
// "Hi NXT,got "
TextOut(0, LCD_LINE6, "rcv: ");
TextOut(24, LCD_LINE6, ByteArrayToStr(inbuffer));
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------
task main() {
int i = 0;
int cnt = 0;
byte outbuffer[];
byte inbuffer[];
char result;
SetSensorType(IN_4, SENSOR_TYPE_HIGHSPEED);
Wait(100);
// we use odd parity on the Arduino side
// see: http://forums.nxtasy.org/index.php?showtopic=3871
RS485Uart(HS_BAUD_##RS485_BAUD, HS_MODE_8_DATA|HS_MODE_O_PARITY|HS_MODE_10_STOP);
Wait(100);
StrToByteArray(MSG, outbuffer);
TextOut(0, LCD_LINE1, "RS485 <> Arduino");
while (true) {
outbuffer[14] = '0' + i;
i++; if (i==10) i = 0;
result = RS485Write(outbuffer);
while (!RS485DataAvailable()) {}
result = RS485Read(inbuffer);
printMsg(inbuffer, cnt);
cnt++; if (cnt==1000) cnt = 0;
Wait(TOWAIT);
}
}
Arduino sketch: (Screenshot)
#include "baudrate.h"
// Pins and wires
// Arduino Wire MAX485
const byte RS485_OUT_PIN = 10; // yellow --> DI
const byte RS485_IN_PIN = 11; // green --> RO
const byte RS485_CTL_PIN = 12; // grey --> RE+DE
// VCC --> VCC
// ------------------------------------------
// NXT Sensor Port 4 Wire MAX485
// DIGIAI1 blue --> B
// DIGIAI0 yellow --> A
// GND black --> GND
const byte RECV_RS485_BIT = B00001000;
const byte SEND_RS485_BIT = B00000100;
#define readRS485inPin (PINB & RECV_RS485_BIT)
const unsigned int BUFLEN = 128;
const unsigned int outnbuf = 12;
byte outBuf[BUFLEN];
byte inBuf [BUFLEN];
unsigned int innbuf;
const char msg[] = "Hi NXT,got ";
const byte SER_TIMEOUT = 7;
unsigned int RS485_LEN;
unsigned int bitDelay;
unsigned int halfBitDelay;
const byte CYCLES = 45;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void serSetup(unsigned long baud) {
pinMode(RS485_OUT_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RS485_OUT_PIN, LOW);
pinMode(RS485_IN_PIN, INPUT);
digitalWrite(RS485_IN_PIN, LOW);
pinMode(RS485_CTL_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RS485_CTL_PIN, LOW);
RS485_LEN = 1000000 / baud;
bitDelay = RS485_LEN - clockCyclesToMicroseconds(CYCLES);
halfBitDelay = RS485_LEN/2 - clockCyclesToMicroseconds(CYCLES);
Serial.print("\nRS-485 configured, ");
Serial.print(baud, DEC);
Serial.print(" Baud, Bit length ");
Serial.print(RS485_LEN, DEC);
Serial.println(" uSec");
}
// Startbit of 1st byte of incoming message encountered
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
byte serAvail() {
return readRS485inPin;
}
// Read a byte
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
unsigned int serRead() {
byte i;
int val = 0;
byte parity = 0, stopbit = 0;
long start = millis();
while (true) {
if (millis()-start>SER_TIMEOUT) return -1;
if (readRS485inPin) break; // startbit hit
}
delayMicroseconds(halfBitDelay); // jump to middle of startbit
for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
delayMicroseconds(bitDelay);
val |= !readRS485inPin << i; // data bits
}
delayMicroseconds(bitDelay);
parity = !readRS485inPin; //
delayMicroseconds(bitDelay);
stopbit = !readRS485inPin; //
return val;
}
// Write one bit
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
void serBit(byte mark) {
if (mark) PORTB &= ~ SEND_RS485_BIT;
else PORTB |= SEND_RS485_BIT;
// delayMicroseconds(RS485_LEN);
delayMicroseconds(bitDelay);
}
// Write a byte
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void serWrite(byte data) {
byte mask = 1;
byte bitcount = 0;
serBit(LOW); // startbit
for (byte i=0; i<8; i++) { // data from LSB to MSB
if (data & mask) {
serBit(HIGH);
bitcount++;
} else {
serBit(LOW);
}
mask <<= 1;
}
serBit((bitcount%2)==0); // odd parity bit
serBit(HIGH); // stop bit
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void printMsg(const char *s, byte buf[], int nbuf) {
Serial.print(s);
Serial.print(": \"");
for (int i=0; i<nbuf; i++)
Serial.print(buf[i], BYTE);
Serial.println("\"");
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void serSendMsg(byte buf[], int nbuf) {
int i;
digitalWrite(RS485_CTL_PIN, HIGH);
for (i=0; i<nbuf; i++)
serWrite(buf[i]);
digitalWrite(RS485_CTL_PIN, LOW);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
int serRecvMsg(byte buf[]) {
int c;
int nbuf = 0;
while ((c = serRead())!=-1)
buf[nbuf++] = c;
return nbuf;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void measureComms(byte stage) {
static unsigned long old = 0;
unsigned long now;
if (!stage) {
old = millis();
} else {
now = millis();
Serial.print("comms took ");
Serial.print(now-old, DEC);
Serial.println(" mSec");
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
for (int i=0; i<outnbuf; i++)
outBuf[i] = msg[i];
outBuf[12] = 0;
serSetup(RS485_BAUD);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
// measureComms(0);
if (serAvail()) {
innbuf = serRecvMsg(inBuf);
outBuf[11] = inBuf[innbuf-1];
serSendMsg(outBuf, outnbuf);
// measureComms(1);
printMsg("Recv", inBuf, innbuf);
printMsg("Sent", outBuf, outnbuf);
}
}
Future ideas:
RCX-bridge with MAX485 only (no Arduino), IR-LED and IR-receiver